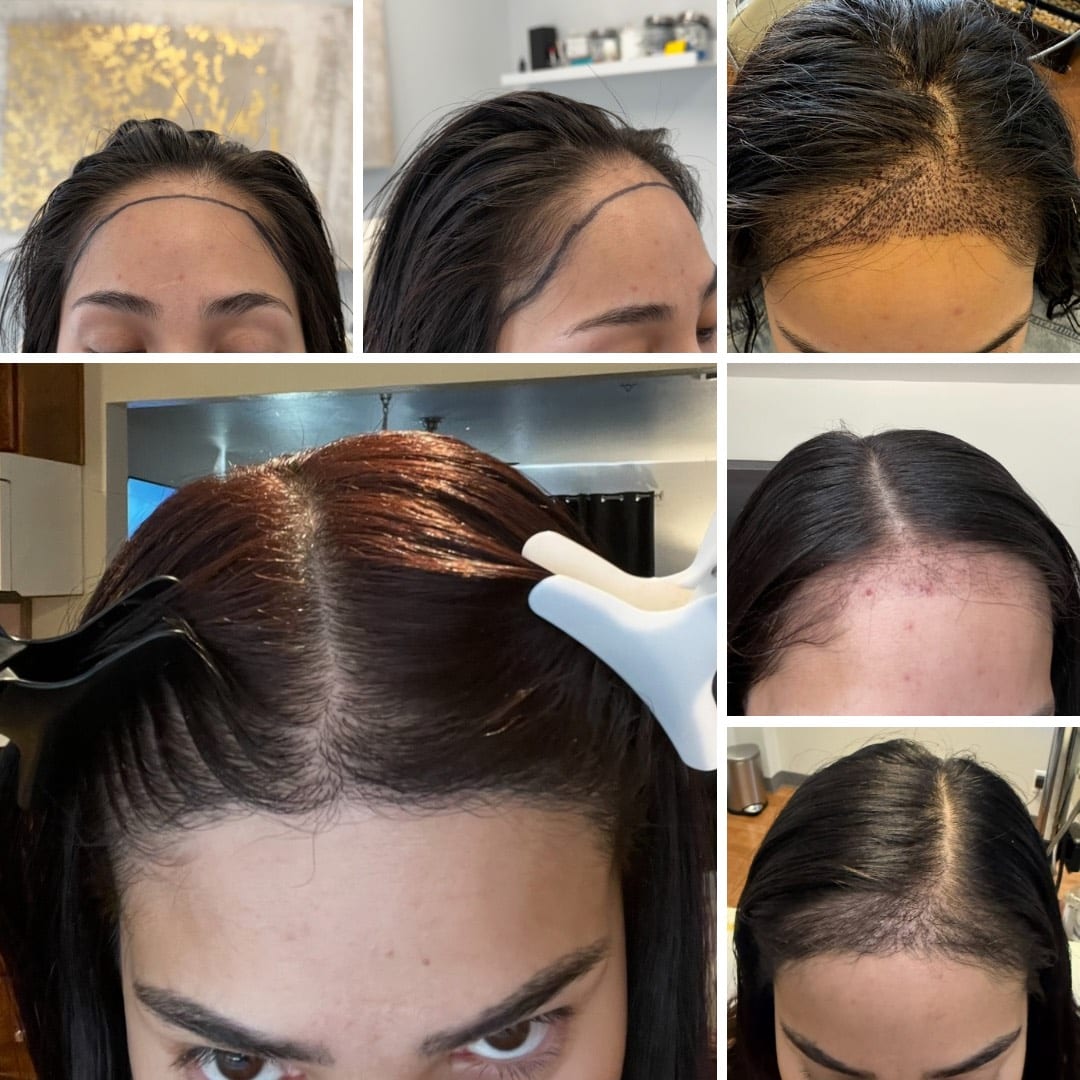
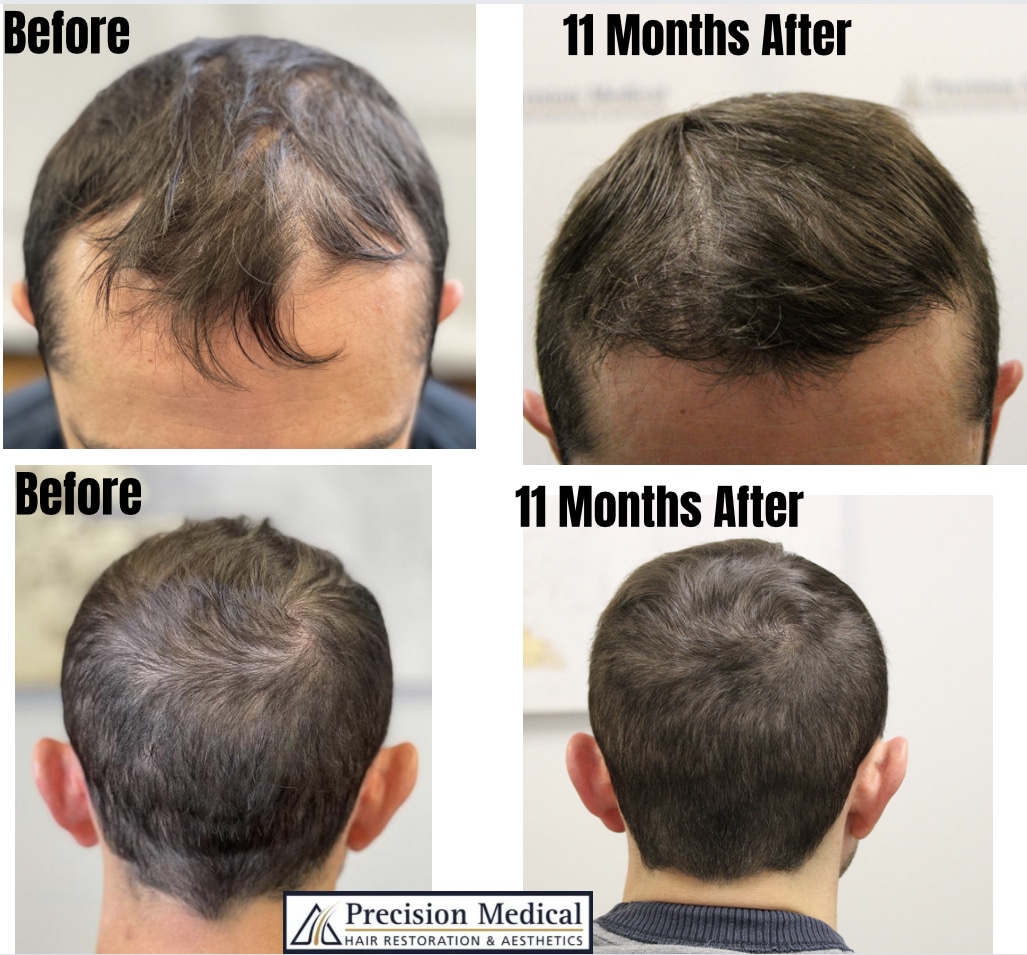
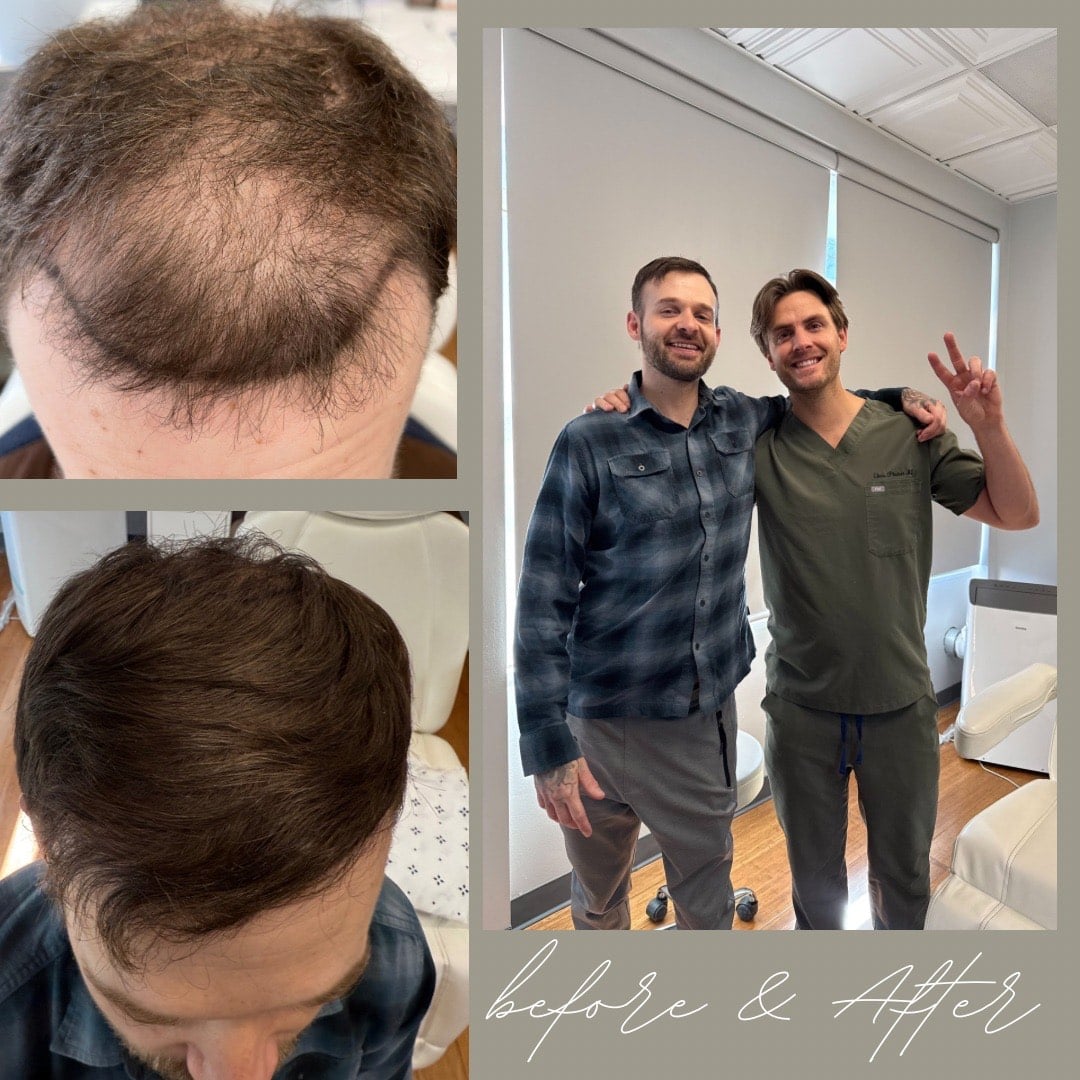
Hair loss is a common concern that affects people of all ages. It's not just a problem for older individuals; it can occur in teenagers, young adults, and middle-aged individuals as well. In fact, studies show that hair loss can begin as early as adolescence and become more prevalent with age.
This blog post will explore the prevalence of hair loss across different age groups and the importance of addressing these concerns at various stages of life. We'll discuss the impact of hair loss on self-esteem and overall well-being, as well as provide practical tips and solutions for managing hair loss at different ages.
Whether you're a teenager experiencing hair thinning or an older adult dealing with age-related hair loss, this post will provide valuable insights and advice to help you address your hair loss concerns effectively.
Understanding Hair Loss:
Hair loss, also known as alopecia, refers to the gradual or sudden loss of hair from the scalp or other parts of the body where hair normally grows. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, medications, and environmental factors.
The hair growth cycle consists of three main phases: anagen (growth phase), catagen (transitional phase), and telogen (resting phase). During the anagen phase, hair actively grows from the follicle. The catagen phase is a transitional period where hair growth slows down, and the follicle shrinks. Finally, during the telogen phase, the hair rests and eventually sheds, making way for new hair growth.
Disruptions in the hair growth cycle can lead to hair loss. For example, excessive physical or emotional stress, hormonal imbalances (such as those experienced during pregnancy or menopause), nutritional deficiencies, and certain medical conditions can prolong the telogen phase or cause more hairs to enter the telogen phase prematurely, resulting in increased shedding and thinning of the hair.
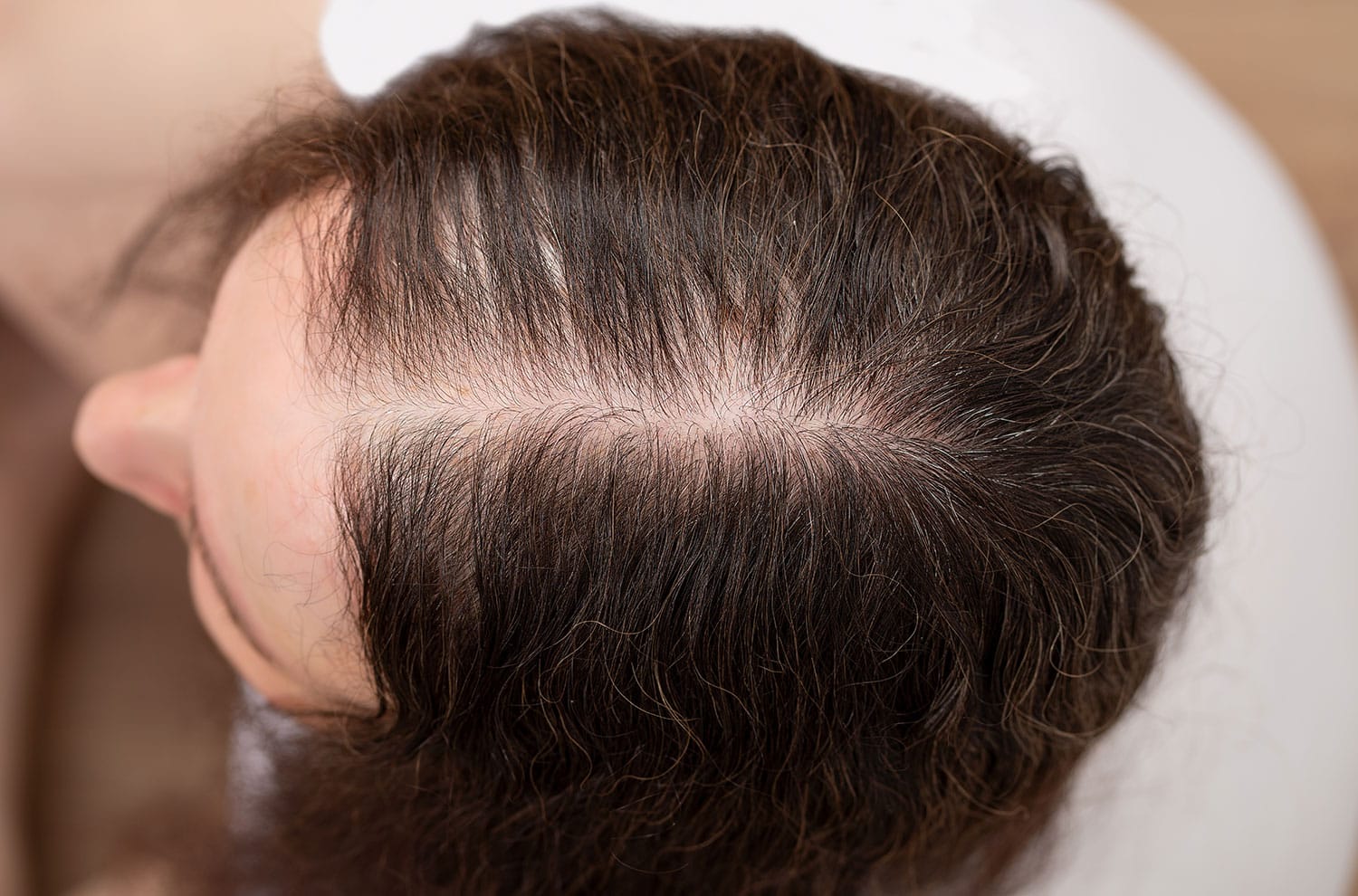
Common types of hair loss include:
- Androgenetic alopecia (male or female pattern baldness): This type of hair loss is primarily genetic and is characterized by a gradual thinning of hair, typically starting at the temples or crown of the head in men and diffuse thinning across the scalp in women.
- Telogen effluvium: This is a temporary form of hair loss caused by a sudden or significant physiological or emotional stressor, such as childbirth, surgery, severe illness, or extreme weight loss. It leads to a large number of hairs entering the telogen phase simultaneously, resulting in increased shedding and noticeable thinning of the hair.
- Alopecia areata: This is an autoimmune condition characterized by the sudden onset of round, smooth patches of hair loss on the scalp or other areas of the body. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, causing hair to fall out.
Understanding these common types of hair loss and their underlying causes is essential for effectively managing and treating the condition. Depending on the type and severity of hair loss, various treatment options, including medications, topical treatments, and procedures like hair transplantation, may be recommended to promote hair regrowth and restore confidence
Hair Loss in Adolescence and Early Adulthood:
Hair loss can be particularly distressing for teenagers and young adults, as it can impact self-esteem and confidence during crucial developmental stages. Several factors can contribute to hair loss in this age group, including hormonal changes, stress, and poor nutrition.
- Hormonal Changes: Adolescence is a period marked by significant hormonal fluctuations, which can affect hair growth and lead to temporary hair shedding. Hormonal imbalances, such as those associated with puberty or conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can contribute to hair thinning or hair loss in teenagers and young adults.
- Stress: High levels of stress, whether from academic pressure, social challenges, or family issues, can also contribute to hair loss in adolescents and young adults. Stress disrupts the hair growth cycle, leading to increased shedding and potential hair thinning over time.
- Poor Nutrition: Inadequate intake of essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and proteins, can compromise hair health and contribute to hair loss. Diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats may lack the nutrients necessary for optimal hair growth, leading to weakened hair follicles and increased shedding.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Hair during Adolescence and Early Adulthood:
- Balanced Diet: Encourage teenagers and young adults to maintain a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients for hair health, including protein, iron, vitamins (especially vitamin D and B vitamins), and minerals like zinc and selenium. Emphasize the importance of eating a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats to support overall health and hair growth.
- Proper Hair Care: Teach proper hair care practices, such as using gentle shampoos and conditioners suitable for their hair type, avoiding excessive heat styling and harsh chemical treatments, and minimizing tight hairstyles that can cause tension and breakage. Regularly trimming the ends of the hair can also help prevent split ends and promote healthy growth.
- Stress Management Techniques: Encourage teenagers and young adults to incorporate stress-reducing activities into their daily routine, such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or spending time outdoors in nature. Encourage open communication and support networks to help them cope with stressors effectively.
- Healthy Lifestyle Habits: Promote other healthy lifestyle habits, such as getting regular exercise, staying hydrated, getting enough sleep, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, as these factors can also influence overall health and hair growth.
By addressing the underlying causes of hair loss and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, teenagers and young adults can promote optimal hair health and reduce the risk of hair thinning or loss during this critical stage of development.
Hair Loss in Middle Age:
Hair loss is a common concern among middle-aged individuals, with a significant proportion of men experiencing male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia. This condition is characterized by a gradual thinning of hair, typically starting at the temples or crown of the head and progressing over time.
- Prevalence of Hair Loss in Middle Age:
-
-
- Male pattern baldness affects approximately 50% of men by the age of 50 and becomes increasingly common with age.
- While less common, women can also experience hair thinning and loss during middle age, often due to hormonal changes associated with menopause.
-
- Factors Contributing to Hair Loss:
-
-
- Genetics play a significant role in male pattern baldness, with inherited sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) being a primary factor. DHT causes miniaturization of hair follicles, leading to shorter and finer hair growth.
- Hormonal changes, particularly fluctuations in testosterone and DHT levels, can exacerbate hair loss in middle age.
- Aging itself can contribute to hair loss as hair follicles gradually become less active and produce thinner, weaker hairs.
-
- Treatment Options for Managing Hair Loss:
-
- Medications: FDA-approved medications such as finasteride (Propecia) and minoxidil (Rogaine) are commonly used to treat male pattern baldness. Finasteride works by blocking the conversion of testosterone to DHT, while minoxidil stimulates hair follicles to promote hair growth.
- Topical Treatments: In addition to minoxidil, topical treatments such as low-level laser therapy (LLLT) and hair growth serums containing ingredients like peptides and antioxidants may help stimulate hair growth and improve hair density.
- Hair Transplantation: For individuals seeking a more permanent solution, hair transplantation procedures, such as follicular unit transplantation (FUT) or follicular unit extraction (FUE), can restore hair density by transplanting hair follicles from areas of the scalp resistant to DHT to areas of thinning or baldness.
It's essential for middle-aged individuals experiencing hair loss to consult with a dermatologist or hair restoration specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on their individual needs and preferences. While hair loss can be a challenging aspect of aging for many people, advances in medical treatments and surgical procedures offer effective options for managing and even reversing hair loss in middle age.
Hair loss can present unique challenges for older adults, as it often coincides with other age-related factors and medical conditions. Here, we'll explore these challenges and discuss strategies for coping with hair loss in seniors.
Hair Loss in Older Adults:
- Challenges of Dealing with Hair Loss in Older Adults:
- Age-related factors: As individuals age, the rate of hair growth slows down, and hair follicles may produce thinner, weaker hairs. Additionally, changes in hormone levels and reduced blood circulation to the scalp can contribute to hair loss.
- Medical conditions: Older adults may be more susceptible to medical conditions that can cause or exacerbate hair loss, such as thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, and nutritional deficiencies. Chronic illnesses and medications used to treat them can also affect hair health.
- Strategies for Coping with Hair Loss in Seniors:
- Acceptance: Accepting changes in hair appearance as a natural part of aging can help seniors maintain a positive self-image and confidence. Emphasize the importance of focusing on inner qualities and overall well-being rather than external appearance.
- Self-care practices: Encourage seniors to prioritize self-care practices that promote scalp and hair health, such as gentle scalp massages to improve blood circulation, using mild shampoos and conditioners suitable for aging hair, and protecting hair from environmental damage (e.g., sun exposure, harsh weather).
- Alternative styling options: Seniors can explore alternative styling options to enhance their appearance and boost confidence, such as wearing hats, scarves, or wigs to conceal hair loss if desired. Shorter hairstyles or hairstyles that add volume and texture can also help create the illusion of thicker hair.
- Dietary and lifestyle modifications: Encourage seniors to maintain a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support hair health, such as protein, vitamins (especially B vitamins and vitamin D), and minerals like iron and zinc. Regular exercise, adequate hydration, and stress management techniques can also contribute to overall well-being and hair health.
By adopting these coping strategies and maintaining a positive outlook, older adults can effectively manage the challenges associated with hair loss and embrace their unique appearance with confidence and grace. Additionally, seeking support from loved ones, healthcare professionals, or support groups can provide valuable emotional support and encouragement throughout the journey of coping with hair loss in seniors.
Addressing Hair Loss Concerns:
Addressing hair loss concerns can be a significant challenge, but there are steps individuals can take at any age to manage and cope with this issue effectively.
Consult with a Healthcare Professional:
- It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist or a hair specialist, to determine the underlying cause of hair loss and develop a personalized treatment plan. They can perform a thorough evaluation, including medical history, physical examination, and possibly laboratory tests, to identify potential contributing factors.
- Based on the assessment, healthcare professionals like those at Precision Medical Hair Restoration & Aesthetics can recommend appropriate treatment options, which may include medications, topical treatments, lifestyle modifications, or surgical procedures like hair transplantation. They can also provide guidance on managing underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to hair loss.
Explore Treatment Options:
- Treatment options for hair loss vary depending on the cause and severity of the condition. In addition to medical interventions, individuals can explore alternative therapies such as herbal supplements, essential oils, or acupuncture, although the effectiveness of these treatments may vary.
- It's essential to approach treatment with realistic expectations and patience, as hair regrowth may take time, and results can vary from person to person. Consistency and adherence to the treatment plan are key to achieving optimal outcomes.
Maintain a Positive Self-Image:
- While coping with hair loss can be challenging, maintaining a positive self-image is crucial. It's essential to focus on inner qualities, talents, and accomplishments rather than external appearance alone. Engage in activities and hobbies that bring joy and fulfillment, and surround yourself with supportive friends and family who appreciate you for who you are beyond your physical appearance.
- Practice self-care and self-compassion by treating yourself with kindness and acceptance. Remember that hair loss does not define your worth or identity as a person.
Seek Support from Loved Ones:
- Seeking support from loved ones can provide emotional reassurance and encouragement during times of hair loss concerns. Share your feelings and concerns with trusted friends, family members, or support groups who can offer empathy, understanding, and practical advice.
- Open communication and mutual support can strengthen relationships and foster a sense of belonging and acceptance, reducing feelings of isolation or insecurity related to hair loss.
By taking proactive steps to address hair loss concerns, maintaining a positive self-image, and seeking support from loved ones and healthcare professionals, individuals can navigate this challenging experience with resilience and confidence, embracing their unique beauty and inner strength.
Summary
Hair loss is a common concern that can affect individuals at any stage of life, from adolescence to older adulthood. Understanding the underlying causes of hair loss, such as genetics, hormonal changes, stress, and aging, is crucial for effective management. Common types of hair loss include androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, and alopecia areata, each with its own set of contributing factors and treatment options.
Addressing hair loss concerns at every stage of life is essential for maintaining overall well-being and self-esteem. Consulting with healthcare professionals, exploring treatment options, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits can help individuals manage hair loss effectively and promote hair regrowth.
It's important for individuals to maintain a positive self-image and seek support from loved ones throughout their hair loss journey. Embracing one's unique beauty and focusing on inner qualities can help individuals cope with hair loss and maintain confidence and self-assurance.
Reiterating Importance:
Addressing hair loss concerns at every stage of life is crucial for maintaining overall well-being and self-esteem. By taking proactive steps to manage hair loss and seeking support from healthcare professionals and loved ones, individuals can navigate this challenging experience with resilience and confidence.
I encourage readers to take proactive steps to manage their hair loss and embrace their unique beauty. Remember that hair loss does not define your worth or identity. Focus on inner qualities, practice self-care, and seek support from loved ones to navigate this journey with confidence and resilience. For a free hair consultation, please schedule an appointment with Precision Medical Hair Restoration & Aesthetics.
References:
American Academy of Dermatology. (n.d.). Hair Loss. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/hair-and-scalp-problems/hair-loss
Mayo Clinic. (2022). Hair Loss. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hair-loss/symptoms-causes/syc-20372926
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. (2016). Alopecia Areata. https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/alopecia-areata
Sinclair, R. (2016). Female pattern hair loss: a pilot study investigating combination therapy with low-dose oral minoxidil and spironolactone. International Journal of Dermatology, 55(7), 1-4.